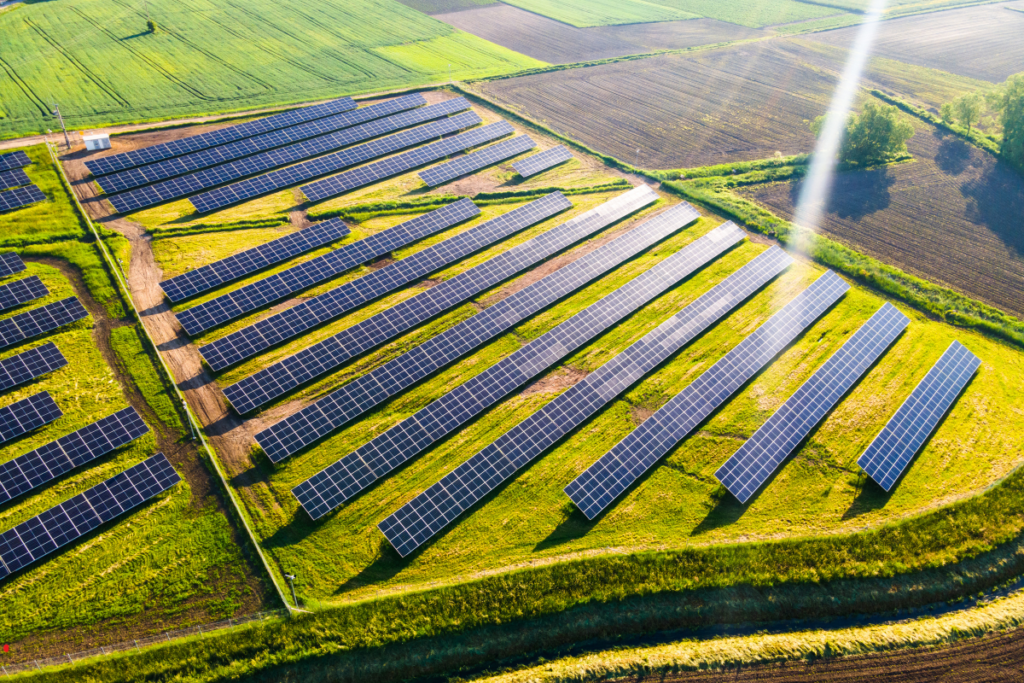
Choosing the right PV mounting system is one of the most important decisions when developing a solar farm. It directly impacts the efficiency, durability, and return on investment of the entire project. A well-designed mounting structure ensures that solar panels operate at their maximum potential, withstand harsh weather conditions, and require minimal maintenance over time. On the other hand, a poor choice can lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and structural failures.
With so many mounting solutions available, selecting the best one can be overwhelming. It all depends on the location, budget, energy goals, and long-term strategy. Understanding the different types of mounting systems and how they perform under various conditions is key to making the right decision.
Why the Right PV Mounting System Matters
At first glance, a solar panel mounting system may seem like a simple structural component, but it plays a much bigger role. It determines how efficiently solar panels capture sunlight, how resistant the installation is to environmental factors, and how easy (or difficult) the system is to maintain.
For example, in regions with strong winds or heavy snowfall, the mounting structure needs to be robust and engineered to withstand extreme conditions. In areas with variable sun exposure, a tracking system may significantly increase energy production. Costs also come into play—some systems require higher upfront investments but provide better long-term returns, while others may be cheaper but offer lower efficiency.
A poorly chosen system can lead to lower energy output, increased maintenance costs, and even potential failures. That’s why understanding the options available is crucial.
Different Types of PV Mounting Systems
There are three main categories of solar mounting structures used in commercial and utility-scale solar farms: fixed-tilt systems, single-axis trackers, and dual-axis trackers. Each has its own advantages, depending on the specific project requirements.
Fixed-Tilt Ground-Mounted Systems
The most common and cost-effective option, fixed-tilt systems keep solar panels at a constant angle, usually optimized for the site’s latitude. These systems are widely used in large-scale solar farms because they are simple, reliable, and easy to install.
Fixed-tilt structures require little maintenance, as they have no moving parts. However, they don’t adjust to the sun’s position, which means they can’t capture as much energy as tracking systems. Despite this, in locations with stable, high solar radiation, they remain a cost-effective and efficient choice.
Single-Axis and Dual-Axis Tracking Systems
Unlike fixed-tilt systems, solar trackers move the panels to follow the sun’s path throughout the day. Single-axis trackers adjust on one plane, typically east to west, while dual-axis trackers move both horizontally and vertically to maximize solar exposure.
The benefit of using a tracking system is clear: higher energy yield. By constantly adjusting the panel’s angle to face the sun directly, single-axis trackers can increase energy output by 15-30%, while dual-axis trackers can boost it even further.
However, this increased efficiency comes at a price. Tracking systems are more expensive to install and have higher maintenance costs due to their moving parts. In regions with frequent storms or extreme weather, they may also be more vulnerable to damage. Despite this, for projects where maximizing output is the priority, trackers offer a strong return on investment.
Bifacial PV Mounting Systems
Another emerging trend in solar farm design is the use of bifacial panels, which generate power from both the front and back sides by capturing reflected sunlight. These panels require specialized mounting structures that allow light to reach the underside of the panel.
In the right conditions, bifacial systems can increase total energy production by 5-20%. They are particularly effective in locations with high ground reflectivity, such as snowy regions, deserts, or sites with reflective surfaces like white gravel. While they may require a slightly higher investment, the additional energy output can significantly improve the project’s overall profitability.
How to Choose the Best PV Mounting System for Your Solar Farm
There’s no single answer to what the best PV mounting system is—it depends entirely on the project’s location, goals, and budget. However, a few key factors can help guide the decision:
Site Conditions and Climate
The geographical location of the solar farm plays a major role in determining the most suitable mounting structure. In regions with high wind speeds, a low-profile fixed-tilt system with strong foundations might be the best option. In areas with high solar variability, single or dual-axis trackers could significantly boost energy production.
The soil type is another important factor. Some mounting systems require deep foundations, which might not be feasible in rocky or unstable terrain. In such cases, ballasted systems that don’t require ground penetration might be a better solution.
Energy Goals and Budget
Every solar farm has different objectives. If the primary goal is to keep costs low, a fixed-tilt system will provide a stable, low-maintenance solution. If the priority is maximum efficiency and long-term energy generation, tracking systems or bifacial setups will deliver the best results.
It’s also important to consider maintenance costs. While trackers can boost efficiency, they require regular servicing to keep the moving parts in good condition. Factoring in both upfront and long-term costs is crucial to making a profitable decision.
Finding a Reliable Manufacturer
Not all PV mounting systems are created equal. A low-quality mounting structure can lead to serious issues, including misalignment, instability, and even system failures. When choosing a supplier, it’s essential to look for:
- High-quality materials – Corrosion-resistant steel or aluminum ensures long-term durability.
- Wind and snow load certifications – Compliance with local weather conditions is key for safety.
- Ease of installation – A well-designed mounting system reduces labor costs and speeds up deployment.
Final Thoughts
The PV mounting system is the foundation of any solar farm, directly affecting its efficiency, durability, and financial success. Whether opting for a fixed-tilt system, a tracking solution, or a bifacial mounting setup, the decision should be based on the site’s characteristics, energy production goals, and long-term financial strategy.
Investing in the right mounting system ensures that solar panels operate at peak efficiency, withstand environmental challenges, and deliver strong returns for decades to come.



